History
“The more you know about the past, the better prepared you are for the future.”
- Theodore Roosevelt
Purpose
A high-quality history education will help pupils gain a coherent knowledge and understanding of Britain’s past and that of the wider world. It should inspire pupils’ curiosity to know more about the past. Teaching should equip pupils to ask perceptive questions, think critically, weigh evidence, sift arguments, and develop perspective and judgement. History helps pupils to understand the complexity of people’s lives, the process of change, the diversity of societies and relationships between different groups, as well as their own identity and the challenges of their time.
Aims
The national curriculum for history aims to ensure that all pupils:
- know and understand the history of these islands as a coherent, chronological narrative, from the earliest times to the present day: how people’s lives have shaped this nation and how Britain has influenced and been influenced by the wider world
- know and understand significant aspects of the history of the wider world: the nature of ancient civilisations; the expansion and dissolution of empires; characteristic features of past non-European societies; achievements and follies of mankind
- gain and deploy a historically grounded understanding of abstract terms such as ‘empire’, ‘civilisation’, ‘parliament’ and ‘peasantry’
- understand historical concepts such as continuity and change, cause and consequence, similarity, difference and significance, and use them to make connections, draw contrasts, analyse trends, frame historically valid questions and create their own structured accounts, including written narratives and analyses
- understand the methods of historical enquiry, including how evidence is used rigorously to make historical claims, and discern how and why contrasting arguments and interpretations of the past have been constructed
- gain historical perspective by placing their growing knowledge into different contexts: understanding the connections between local, regional, national and international history; between cultural, economic, military, political, religious and social history; and between short- and long-term timescales
Intent
St Michaels history curriculum aims to inspire pupils to be curious and creative thinkers who develop a complex knowledge of local and national history and the history of the wider world. We want pupils to develop the confidence to think critically, ask questions, and be able to explain and analyse historical evidence.
Through our lessons, we aim to build an awareness of significant events and individuals in global, British and local history and recognise how things have changed over time. History will support children to appreciate the complexity of people’s lives, the diversity of societies and the relationships between different groups. Studying History allows children to appreciate the many reasons why people may behave in the way they do, supporting children to develop empathy for others while providing an opportunity to learn from mankind’s past mistakes. Learning in History aims to support pupils in building their understanding of chronology in each year group, making connections over periods of time and developing a chronologically-secure knowledge of History. We hope to develop pupils’ understanding of how historians study the past and construct accounts and the skills to carry out their own historical enquiries. In order to prepare pupils for their future learning in History, our scheme aims to introduce them to key substantive concepts including power, invasion, settlement and migration, empire, civilisation, religion, trade, achievements of humankind, society and culture. St Michael’s history curriculum enables pupils to meet the end of Key stage attainment targets in the National curriculum and the aims also align with those set out in the National curriculum. For EYFS, the activities allow pupils to work towards the Understanding the world Development matters statements and Early learning goals, while also covering foundational
knowledge that will support them in their further history learning in Key stage 1.
Implementation
In order to meet the aims of the National curriculum for History and in response to the Ofsted Research review into History, we have identified the following key strands:
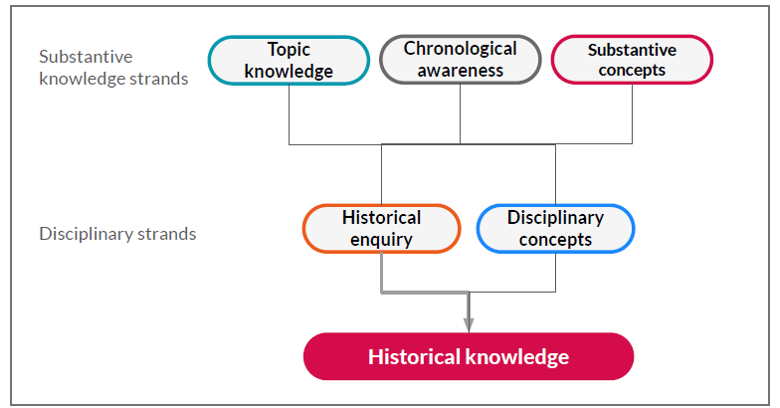
The curriculum emphasises the importance of historical knowledge being shaped by disciplinary approaches, as shown in the diagram above. These strands are interwoven through all our History units to create engaging and enriching learning experiences which allow the children to investigate history as historians do.
Each six-lesson unit has a focus on chronology to allow children to explore the place in time of the period they are studying and make comparisons in other parts of the world. In EYFS, children explore the concept of history by reflecting on key experiences from their own past, helping them understand that they each have their own histories. Then, they engage in activities to compare and contrast characters from stories, including historical figures, deepening their understanding of how individual lives fit into broader historical narratives. Children will further develop their awareness of the past in Key stage 1 and will know where people and events fit chronologically. This will support children in building a ‘mental timeline’ they can refer to throughout their learning in Key stage 2 and identifying connections, contrasts and trends over time. At St Michael’s, each child has a KS1 or KS2 timeline in the front of their books to refer back to at the beginning of each new unit, which supports children in developing this chronological awareness.
There are two EYFS units focused on each of the history-related Development matters statements. These units consist of a mixture of adult-led and child-initiated activities which can be selected by the teacher to fit in with Reception class themes or topics. In Key stage 1 and 2, units are organised around an enquiry-based question and children are encouraged to follow the enquiry cycle (Question, Investigate, Interpret, Evaluate and conclude, Communicate) when answering historical questions.
Over the course of the scheme, children develop their understanding of the following key disciplinary concepts:
• Change and continuity.
• Cause and consequence.
• Similarities and differences.
• Historical significance.
• Historical interpretations.
• Sources of evidence.
These concepts will be encountered in different contexts during the study of local, British and world history. Accordingly, children will have varied opportunities to learn how historians use these skills to analyse the past and make judgements. They will confidently develop and use their own historical skill set. As children progress through the curriculum, they will create their own historical enquiries to study using sources and the skills they have developed.
Substantive concepts such as power, trade, invasion and settlement, are introduced in Key stage 1, clearly identified in Lower key stage 2 and revisited in Upper key stage 2 (see Progression of skills and knowledge) allowing knowledge of these key concepts to grow. These concepts are returned to in different contexts, meaning that pupils begin to develop an understanding of these abstract themes which are crucial to their future learning in History.
The history curriculum follows the spiral curriculum model where previous skills and knowledge are returned to and built upon. For example, children progress by developing their knowledge and understanding of substantive and disciplinary concepts by experiencing them in a range of historical contexts and periods. History in Action videos explain the careers and work of those in history and heritage-related fields. Historians, archivists, archaeologists, museum curators, teachers and heritage experts discuss their love of history, how they became interested in the subject, how they got into their jobs and what their jobs involve. Visitors from the local community offer further enrichment opportunities.
Lessons are designed to be varied, engaging and hands-on, allowing children to experience the different aspects of an historical enquiry. In each lesson, children will participate in activities involving disciplinary and substantive concepts, developing their knowledge and understanding of Britain’s role in the past and that of the wider world. Children will develop their knowledge of concepts and chronology as well as their in-depth knowledge of the context being studied.
Teachers are encouraged to adapt teaching for every lesson to ensure that lessons can be accessed by all pupils and opportunities to stretch pupils’ learning are available when required.
Knowledge organisers for each unit support pupils in building a foundation of factual knowledge by encouraging recall of key facts, concepts and vocabulary. Strong subject knowledge is vital for staff to be able to deliver a highly-effective and robust history curriculum. Each unit of lessons focuses on the key subject knowledge needed to deliver the curriculum, making links with prior learning and identifying possible misconceptions.
Impact
The impact of our curriculum can be constantly monitored through both formative and summative assessment opportunities. Each lesson includes opportunities to support teachers in assessing pupils against the learning objectives. Furthermore, each unit has a skill catcher and knowledge assessment quiz which can be used at the end of the unit to provide a summative assessment. Pupils should leave school equipped with a range of skills to enable them to succeed in their secondary education. They will be enquiring learners who ask questions and can make suggestions about where to find the evidence to answer the question. They will be critical and analytical thinkers who are able to make informed and balanced judgements based on their knowledge of the past.
The expected impact of following the is that children will:
● Know and understand the history of Britain, how people’s lives have shaped this nation and how Britain has influenced and been influenced by the wider world.
● Develop an understanding of the history of the wider world, including ancient civilisations, empires, non-European societies and the achievements of mankind.
● Develop a historically-grounded understanding of substantive concepts - power, invasion, settlement and migration, civilisation, religion, trade, achievements of mankind and society.
● Form historical arguments based on cause and effect, consequence, continuity and change, similarity and differences.
● Have an appreciation for significant individuals, inventions and events that impact our world both in history and from the present day.
● Understand how historians learn about the past and construct accounts.
● Ask historically-valid questions through an enquiry-based approach to learning to create structured accounts.
● Explain how and why interpretations of the past have been constructed using evidence.
● Make connections between historical concepts and timescales.
● Meet the relevant Early Learning Goals at the end of EYFS (Reception) and the end of key stage expectations outlined in the National curriculum for History at the end of Key stage 1 and 2.
Teachers will record results of quizzes, lesson questioning and use outcomes in books, skills catchers and substantive question responses to inform their judgement. Teachers will record their assessments at the end of each unit onto an Excel spreadsheet as formative assessment and then at the end of each year to allow pupil tracking of progress and attainment on Arbor.




